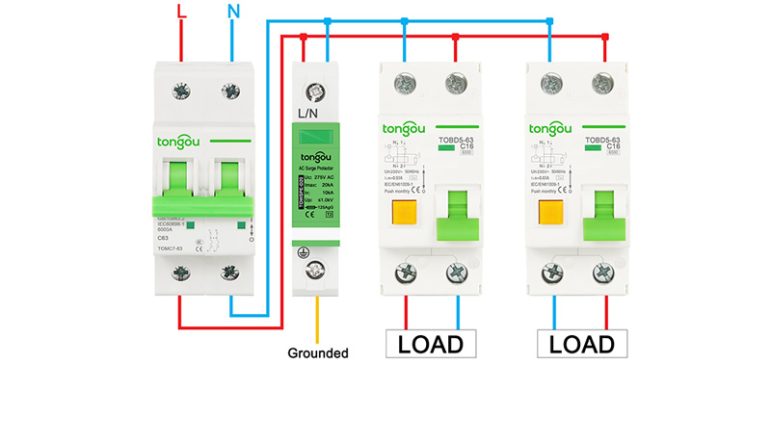
Οι συσκευές προστασίας από υπερτάσεις είναι εξαρτήματα που χρησιμοποιούνται σε συστήματα δεδομένων και ισχύος για την ασφάλεια του υλικού. Επηρεάζονται σε κυκλώματα χαμηλής ισχύος. Ωστόσο, η λειτουργία αυτών των συστημάτων είναι για την πρόληψη καταστροφής ή διακοπής λόγω παροδικών υπερτάσεων.
Τα SPD αφαιρούν ηλεκτρικές υπερτάσεις ή παλμούς λειτουργώντας ως διαδρομή χαμηλής αντίστασης. Έτσι, μετατρέποντας τις παροδικές τάσεις σε ρεύματα και επαναδρομολογώντας τις κατά μήκος του εδάφους. Αυτό γίνεται για να μειωθεί η επίθεση της γραμμής μεταφοράς. Αυτή η συσκευή συνδέεται παράλληλα με τα κυκλώματα τροφοδοσίας των φορτίων που υποτίθεται ότι προστατεύει. Αυτή είναι η πιο ευρέως χρησιμοποιούμενη και αποτελεσματική μέθοδος προστασίας μη ισορροπημένης τάσης.
Οι μεταβατικές τάσεις υπερτάσεων προκαλούνται από τη λειτουργία μεταγωγής ηλεκτρικών φορτίων σε ένα κτίριο, καθώς και από τη μαγνητική και επαγωγική σύζευξη που προκαλείται από το σχηματισμό μαγνητικού πεδίου καθώς ρέουν μεγάλα ρεύματα. Ο στατικός ηλεκτρισμός και οι καταιγίδες μπορούν επίσης να καταλήξουν να προκαλέσουν υπερτάσεις. Καθώς ο κεραυνός είναι μια σημαντική πηγή ηλεκτρομαγνητικών παρεμβολών στα ηλεκτρικά συστήματα.
Υπάρχουν δύο τύποι κεραυνών:
1.The lightning path is directly connected to the power structure transmission lines.
2.Electro – magnetic pairing of energy into electric grid conductors caused by nearby thunder discharge radiant energy.
The principle of operation of Surge Protective Devices (SPDs) is centered on safeguarding electrical systems from transient overvoltages, also known as surges. The main concept is to limit these voltage spikes by either diverting or limiting the surge current. Here’s how it works:
Βαρίστορ οξειδίου μετάλλου (MOV): One of the most common components within an SPD is the metal oxide varistor. A varistor is an electronic component with a resistance that varies with the applied voltage, showcasing a nonlinear, non-ohmic current-voltage characteristic. When the voltage is normal, the MOV has a very high resistance, allowing normal operation of the electrical system. However, during a surge event, the MOV’s resistance drops dramatically, becoming very low. This change allows the MOV to “absorb” excess voltage and then act as a “shunt” by diverting the excess current away from the protected load and safely to the ground.
How SPDs Divert Current:
1.When a voltage spike occurs, the SPD quickly reacts, creating a low-impedance (low-resistance) path to the ground.
2.This diverts the impulse current away from the critical loads.
3.By diverting the current, the SPD also reduces the resulting voltage experienced by the connected equipment to a safer level.
Other Components of SPDs:
SPDs may also use Gas Discharge Tubes (GDTs), Silicon Avalanche Diodes (SADs), or Transient Voltage Suppressor (TVS) Diodes, depending on the specific design and protection requirements.
Result of SPD Action:
By functioning this way, SPDs protect sensitive electronic devices from voltage spikes caused by lightning strikes, power surges, and other types of electrical disturbances.
The goal is to prevent these transients from causing damage or operational issues, extending the lifespan of the equipment and ensuring its functionality.
Selection of SPD:
The proper selection of an SPD is based on several factors including the location within the electrical system, the types of surges expected, and the vulnerability of the connected equipment.
The selection criteria involve the SPD’s Maximum Continuous Operating Voltage (MCOV), Nominal Discharge Current (In), and Voltage Protection Rating (VPR), among other parameters.
1.SPD type 1
Type 1 SPDs are installed at the service entrance of a building’s electrical system. Their primary function is to shield against large surges, typically originating from external sources, such as direct lightning strikes. They are the first line of defense and can dissipate high-energy impacts. In terms of installation, Type 1 SPDs are mounted on the line side of the main service entrance panel, between the utility pole and where the electrical service enters the building.
2.SPD type 2
Type 2 SPDs are used in the main distribution board (or at sub-distribution boards) and are designed to manage surges that originate from within the building, such as those caused by large equipment switching on and off. These SPDs provide protection to circuits and devices downstream and are particularly important in safeguarding sensitive electronic equipment. They manage the surges that Type 1 SPDs may not fully divert, capturing smaller, repetitive surges that may otherwise degrade or damage connected devices over time.
3.SPD type 3
Type 3 SPDs are installed at the point of use – close to the end-use devices they’re meant to protect, such as computers, televisions, or other electronic appliances. They are generally used in conjunction with Type 2 SPDs for a more comprehensive protection strategy. They are designed to suppress the remaining surge energy after Type 2 SPDs have functioned, therefore dealing with surges that infiltrate into individual pieces of equipment.
4.Combined Type 1+2 SPDs
Some SPDs combine features of both Type 1 and Type 2 devices. These Type 1+2 SPDs can protect all electrical installations against lightning strikes by discharging the current and are suited for locations with a high density of lightning strikes.
1. Large Protection Flow: SPDs are designed to handle large surge currents, efficiently diverting them to prevent damage to the electrical system and connected devices.
2. Extremely Low Residual Pressure:The residual voltage, or let-through voltage, after the SPD has acted is kept as low as possible. This is the voltage that equipment will actually experience during a surge event, and keeping it low is essential for protection.
3. Fast Response Time: SPDs act swiftly to combat surges, often within nanoseconds, which is crucial to safeguard equipment from the rapid onset of voltage spikes.
4. Arc Extinguishing Technology: Modern SPDs utilize advanced arc extinguishing technologies to prevent any fire hazards that could potentially arise from surge events.
5. Temperature Control Protection Circuit: A built-in circuit that monitors temperature prevents overheating of the SPD components, ensuring stability and preventing thermal runaway or damage.
6. Built-In Thermal Protection: SPDs often have thermal fuses or similar mechanisms to disconnect the SPD from the circuit in the event of overheating, providing an extra layer of safety.
7. Maximum Continuous Operating Voltage (MCOV): The highest voltage an SPD can withstand on a continuous basis without degradation or failure, signifies the SPD’s ability to handle normal voltage fluctuations.
8. Voltage Protection Rating (VPR): This rating indicates the maximum voltage that will be delivered to connected equipment during a surge event after the SPD has functioned.
The field of ‘Surge Protective Devices’ encompasses a broad spectrum of types and applications tailored to varying needs from domestic to industrial scales. Selecting the right SPD calls for a comprehensive understanding of the underlying technology, its applications, and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Αυτές οι τετράγωνες συσκευές βοηθούν στην αποφυγή απώλειας ή τραυματισμού ευαίσθητου εξοπλισμού, ωστόσο είναι απαραίτητες για ασφάλεια. Το Surge Protective είναι απαραίτητο για κάθε επιχειρηματικό, βιομηχανικό ή δημόσιο κτίριο που είναι εξοπλισμένο με εναέριες γραμμές, γεγονός που υποδηλώνει ότι η συντριπτική πλειοψηφία των κτιρίων θα το αναγκάσει. Επιπλέον, θα θέλαμε συσκευές προστασίας από υπερτάσεις καθώς το τετράγωνό τους μετράει τον τύπο ηλεκτρικών προβλημάτων όπως κεραυνούς, διακοπές ρεύματος, δυσλειτουργίες του δικτύου.
When it comes to securing an electrical network, there is no one-size-fits-all strategy. Each setup requires a detailed examination of its ‘Power Surge Causes and Prevention’ mechanisms and a thorough understanding of how the ‘Power Strips vs. Surge Protectors’ debate applies to their specific situation.
Equipped with the knowledge of various SPD types, their applications, and vigilant maintenance practices, one can significantly increase the resilience of their electrical infrastructure against unpredictable and damaging electrical surges.

Η Tongou ιδρύθηκε το 1993, παίρνει τους ειδικούς λύσεων ηλεκτρικών συστημάτων υψηλής τάσης χαμηλής τάσης ως θέση της μάρκας, παίρνει την επίλυση της πίεσης και των προκλήσεων των πελατών ως ευθύνη και δημιουργεί αξία για τους πελάτες.
© 2023 Tongou Electrical. Ολα τα δικαιώματα διατηρούνται.